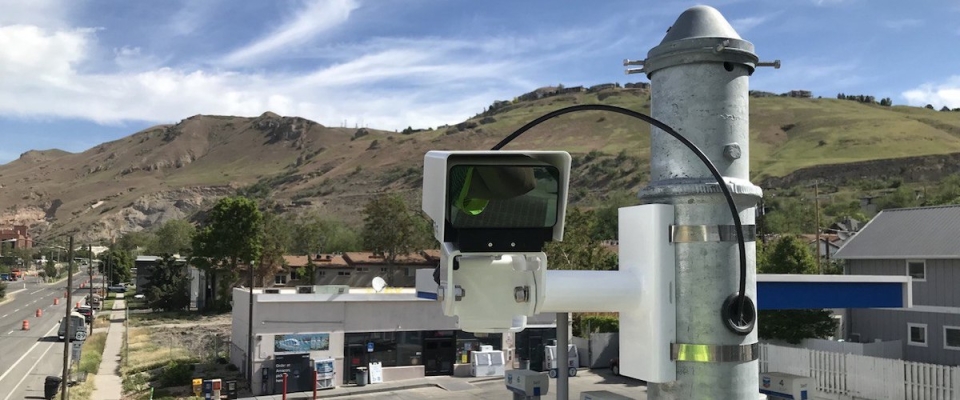
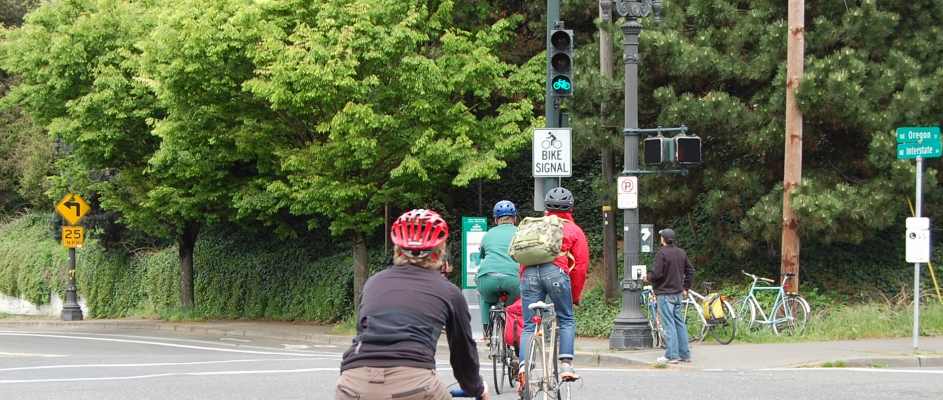
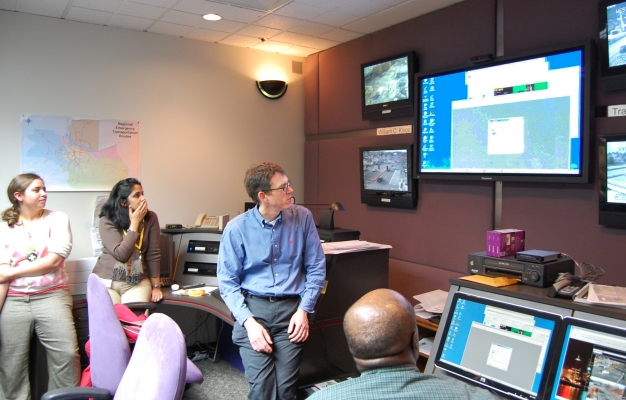
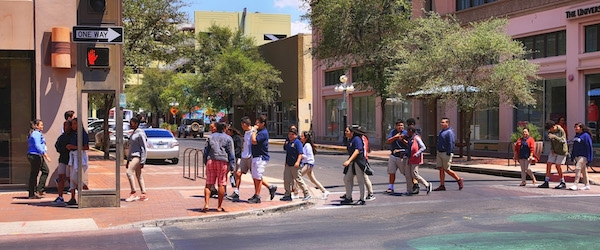Pedestrian safety is critical to improving walkability in cities. To that end, NITC researchers have developed a system for collecting pedestrian behavior data using LiDAR sensors. Tested at two intersections in Texas and soon to be tested at another in Salt Lake City, Utah, the new software created by a multi-university research team is able to reliably observe pedestrian behavior and can help reduce conflicts between pedestrians and vehicles at signalized intersections. The Utah Department of Transportation (UDOT) is already working on implementing this new system to improve data collection at intersections.
Learn more in a free webinar May 18.
The LiDAR system can especially improve multimodal travel at intersections with permissive left turns, which are indicated by a flashing yellow arrow. Previous research has shown that where a flashing yellow arrow, or FYA, is present, cars searching for a gap in traffic may not look for pedestrians. To remove the risk to people walking, some signals are programmed to turn off the FYA when a walk button is pushed. But...
Read more