The video begins at 1:47.
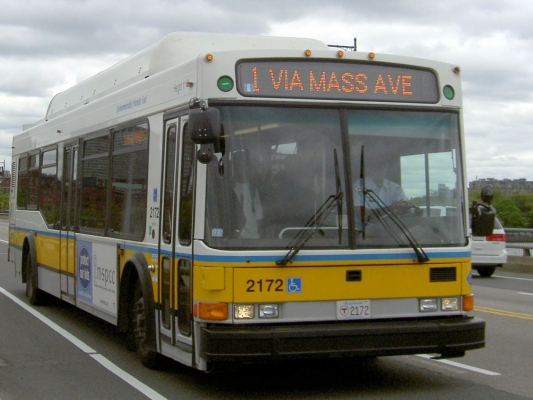
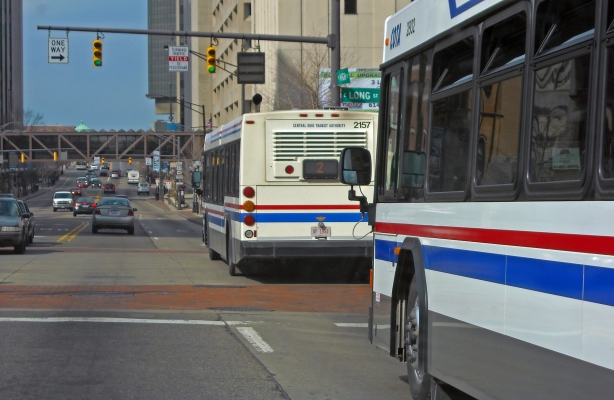
Abstract: In transportation planning and engineering, market segments or groups of individuals with varying attitudes and travel behavior are often identified in order to define a set of policies and strategies targeted at each segment. Examples include residential location choice studies, electric vehicle adoption and the marketing of public transit options. Defining market segments is common in the marketing literature, typically based on observed socioeconomic characteristics, such as gender and income. However, in addition to these characteristics, travelers may also be segmented based on variations in their observed travel and activity patterns. The activity-based approach to travel demand analysis acknowledges the need to analyze the travel patterns of individuals, conceptualized as a trip chain or tour, as opposed to individual trip segments. This has implications for identifying markets segments based on travel patterns which needs to distinguish between the sequencing and timing of travel choices and activities, in addition to the actual travel choices and activities. One approach that holds promise is pattern recognition theory which has wide applications in image analysis, speech recognition and physiological signal processing. In this study, pattern recognition methods are applied to observed daily travel and activity patterns from Oregon to identify travel market...
Read more