Watch video
View slides
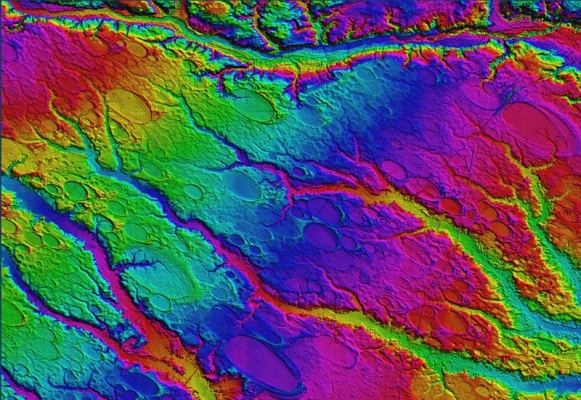
Light detection and ranging (LIDAR) technology is reshaping the civil engineering profession and offers many unique advantages. National efforts such as the 3D Elevation Plan (3DEP) are helping increase the availability of LIDAR data. LIDAR is one of the crucial technologies that is transitioning the world of civil and construction engineering from 2D paper-based design to 3D digital design. The high spatial resolution and accuracy capabilities of LIDAR have led to increased efficiencies, improved analyses, and more informed decision making.
A further advantage of this dataset is that multiple people can use the same dataset for a variety of purposes across multiple disciplines. The visual nature of the dataset also is more intuitive than traditional data acquisition and analysis techniques. This presentation will provide a brief background of LIDAR , its capabilities, limitations and platforms, and discuss its current and future role in civil engineering. Examples of a wide range of transportation, geotechnical, coastal, and structural engineering, science, and planning applications will be presented including development of mobile LIDAR guidelines for...
Read more